CRYPTOCOCCOSIS
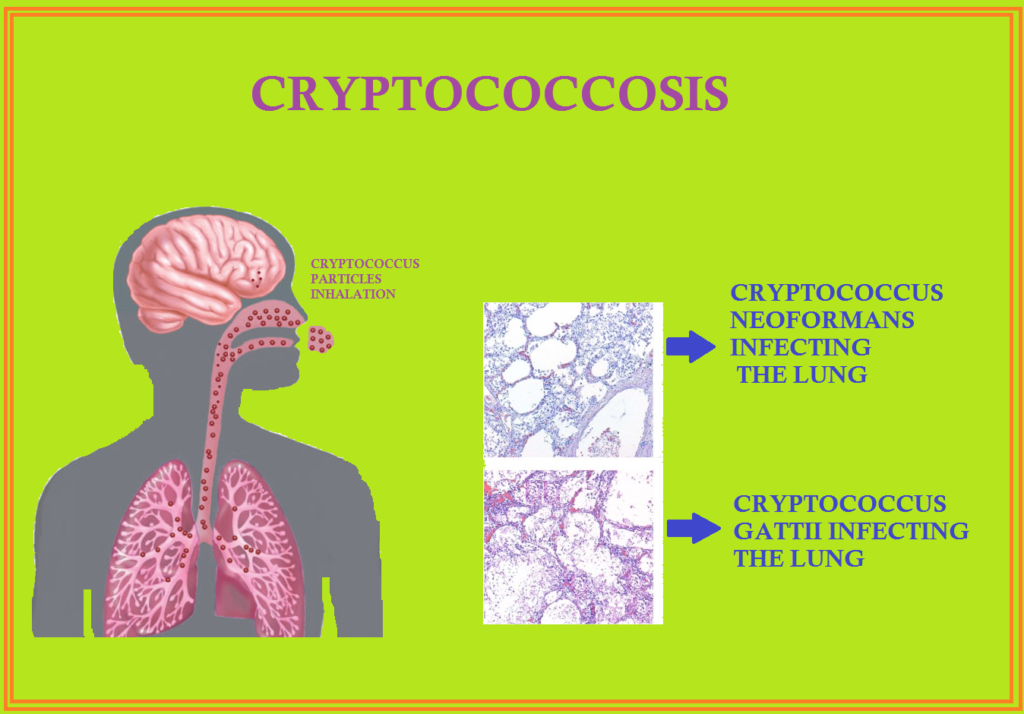
Cryptococcosis is a infection caused by Cryptococcus Neoformans which is a form of yeast that has found worldwide in the soil and also in dried pigeon dung.
Cryptococcus gattii is a species that also cause disease in humans. C-gattii may affect more often immunocompetent persons. Most common cause of fungal meningitis. It is major cause of more severe infections than Cryptococcus Neoformans. Infection is acquired by inhalation. Clinically cryptococcal pneumonia raely develops in immunocompetent persons. Lung disease and dissemination most often occur in setting of Hodgking lymphoma, long term corticosteroid treatment, organ transplant, HIV infection and immunodeficiency.
Pulmonary disease is likely simple nodules to wide spread infiltrates leading to respiratory failure. Disseminating disease may involve any organ. Confusion and mental status changing, nausea, vomiting, and cranial nerve abnormalities is likely be seen as the disease progressed. headache is usually the first symptoms of meningitis.
Cryptococcus gattii infections frequently present with respiratory symptoms along with neurologic signs caused by lesions in CNS. Cryptococcus neoformans infection of the skin may mimic bacterial cellulitis.
Culture test of pleural fluid and respiratory secretions are done for diagnosing of respiratory tract disease. Lumbar puncture is used for diagnosing for suspected meningitis. Gram stain of the CSF usually finds budding, encapsulated fungi. Patients of HIV, the serum cryptococcal antigen is also a sensitive screening test for meningitis, being positive in most of the cases.
To find CNS abnormalities like Cryptococcomas, MRI is more sensitive than CT scan.
Factors that responsible for poor prognosis is organ failure, lack of spinal fluid like pleocytosis, presence of disease outside the nervous system.
TREATMENT
Liposomal amphotericin B, intravenously for 14 days is preferred agent for starting therapy and followed by fluconazole 400MG per day for 8 weeks. This therapy is effective and achieving clinical response and CSF sterilization in most of the patients. In addition of Flucytosine is given for improved survival but toxicity is common. Hematologic parameters must closely monitored during flucytosine therapy and flucytosine dose is adjusted for any decrease in kidney functions.
Frequent repeated lumbar punctures and ventricular shunting must be done to relieve high CSF pressures or if hydrocephalus is a complication. Corticosteroid should not be used.
For Informational purpose only. Consult your Physician for advice.